How to create custom Ubuntu live from scratch
This procedure works and can create a bootable and installable Ubuntu Live (along with the automatic hardware detection and configuration) from scratch.
Prerequisites (GNU/Linux Debian/Ubuntu)
Install applications we need to build the environment.
sudo apt-get install \
debootstrap \
squashfs-tools \
xorriso \
grub-pc-bin \
grub-efi-amd64-bin \
mtools
mkdir $HOME/live-ubuntu-from-scratch
Bootstrap and Configure Ubuntu
-
Checkout bootstrap
sudo debootstrap \ --arch=amd64 \ --variant=minbase \ bionic \ $HOME/live-ubuntu-from-scratch/chroot \ http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/debootstrap is used to create a Debian base system from scratch, without requiring the availability of dpkg or apt. It does this by downloading .deb files from a mirror site, and carefully unpacking them into a directory which can eventually be chrooted into.
-
Configure external mount points
sudo mount --bind /dev $HOME/live-ubuntu-from-scratch/chroot/dev sudo mount --bind /run $HOME/live-ubuntu-from-scratch/chroot/runAs we will be updating and installing packages (among them grub), these mount points are necessary inside the chroot environment, so we can be able to finish the installations without errors.
Define chroot environment
A chroot on Unix operating systems is an operation that changes the apparent root directory for the current running process and its children. A program that is run in such a modified environment cannot name (and therefore normally cannot access) files outside the designated directory tree. The term "chroot" may refer to the chroot(2) system call or the chroot(8) wrapper program. The modified environment is called a chroot jail.
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chroot
- Access chroot environment
sudo chroot $HOME/live-ubuntu-from-scratch/chroot
-
Configure mount points
mount none -t proc /proc mount none -t sysfs /sys mount none -t devpts /dev/pts export HOME=/root export LC_ALL=C -
Set a custom hostname
echo "ubuntu-live" > /etc/hostname -
Configure apt sources.list
cat <<EOF > /etc/apt/sources.list deb http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ bionic main restricted universe multiverse deb-src http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ bionic main restricted universe multiverse deb http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ bionic-security main restricted universe multiverse deb-src http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ bionic-security main restricted universe multiverse deb http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ bionic-updates main restricted universe multiverse deb-src http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ bionic-updates main restricted universe multiverse EOF -
Update indexes packages
apt-get update -
Install systemd
apt-get install -y systemd-sysvsystemd is a system and service manager for Linux. It provides aggressive parallelization capabilities, uses socket and D-Bus activation for starting services, offers on-demand starting of daemons, keeps track of processes using Linux control groups, maintains mount and automount points and implements an elaborate transactional dependency-based service control logic.
-
Configure machine-id and divert
dbus-uuidgen > /var/lib/dbus/machine-id ln -fs /var/lib/dbus/machine-id /etc/machine-idThe
/etc/machine-idfile contains the unique machine ID of the local system that is set during installation or boot. The machine ID is a single newline-terminated, hexadecimal, 32-character, lowercase ID. When decoded from hexadecimal, this corresponds to a 16-byte/128-bit value. This ID may not be all zeros.dpkg-divert --local --rename --add /sbin/initctl ln -s /bin/true /sbin/initctldpkg-divert is the utility used to set up and update the list of diversions.
-
Install packages needed for Live System
apt-get install -y \ ubuntu-standard \ casper \ lupin-casper \ discover \ laptop-detect \ os-prober \ network-manager \ resolvconf \ net-tools \ wireless-tools \ wpagui \ locales \ linux-generic -
Graphical installer
apt-get install -y \ ubiquity \ ubiquity-casper \ ubiquity-frontend-gtk \ ubiquity-slideshow-ubuntu \ ubiquity-ubuntu-artwork -
Install window manager
apt-get install -y \ plymouth-theme-ubuntu-logo \ ubuntu-gnome-desktop \ ubuntu-gnome-wallpapers -
Install useful applications
apt-get install -y \ clamav-daemon \ terminator \ apt-transport-https \ curl \ vim \ nano -
Install Visual Studio Code
-
Download and install the key
curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | gpg --dearmor > microsoft.gpg install -o root -g root -m 644 microsoft.gpg /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/ echo "deb [arch=amd64] https://packages.microsoft.com/repos/vscode stable main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/vscode.list rm microsoft.gpg -
Then update the package cache and install the package using
apt-get update apt-get install -y code
-
-
Install Google Chrome
-
Download and install the key
wget -q -O - https://dl-ssl.google.com/linux/linux_signing_key.pub | sudo apt-key add - echo "deb http://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb/ stable main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list -
Then update the package cache and install the package using
apt-get update apt-get install google-chrome-stable
-
-
Install Java JDK 8
apt-get install -y \ openjdk-8-jdk \ openjdk-8-jre -
Remove unused applications
apt-get purge -y \ transmission-gtk \ transmission-common \ gnome-mahjongg \ gnome-mines \ gnome-sudoku \ aisleriot \ hitori -
Remove unused packages
apt-get autoremove -y -
Reconfigure packages
-
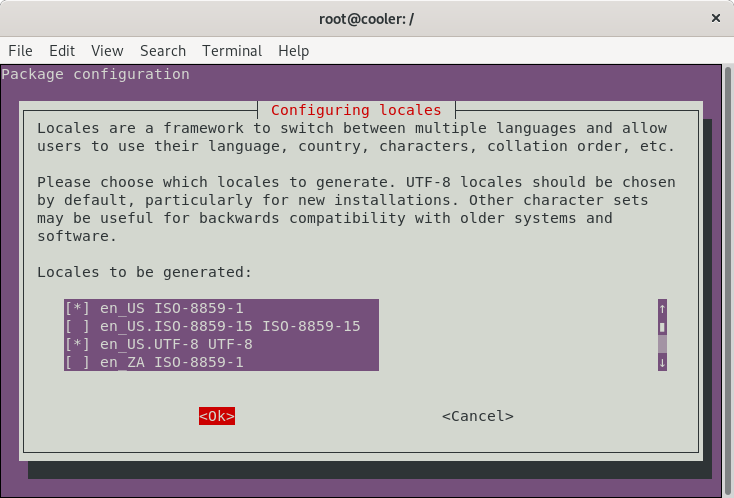
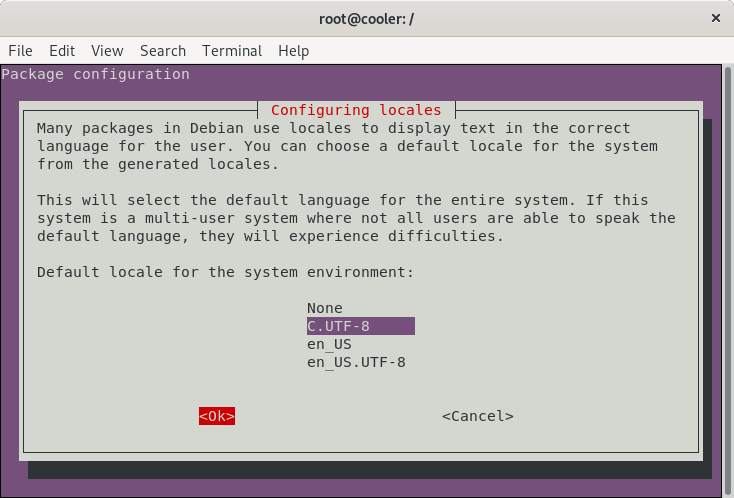
Generate locales
dpkg-reconfigure locales -
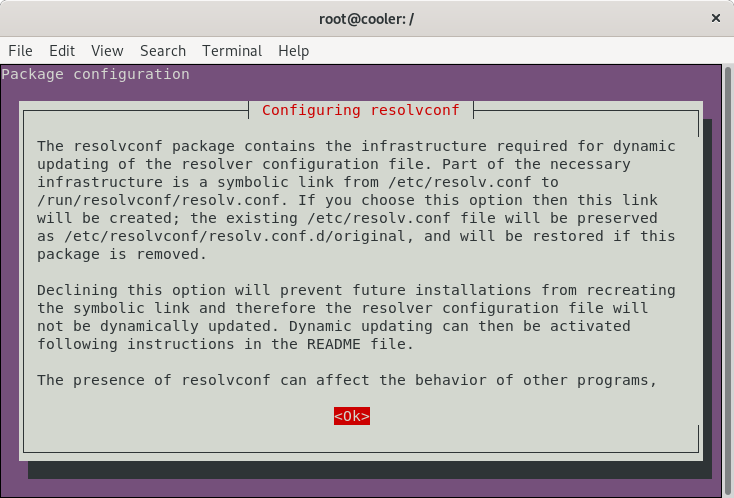
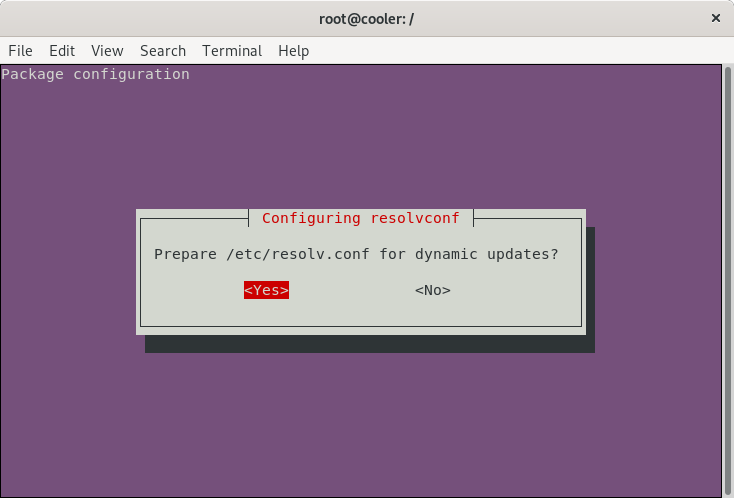
Reconfigure resolvconf
dpkg-reconfigure resolvconf -
Configure network-manager
cat <<EOF > /etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.conf [main] rc-manager=resolvconf plugins=ifupdown,keyfile dns=dnsmasq [ifupdown] managed=false EOF -
Reconfigure network-manager
dpkg-reconfigure network-manager
-
-
Cleanup the chroot environment
-
If you installed software, be sure to run
rm /var/lib/dbus/machine-id -
Remove the diversion
rm /sbin/initctl dpkg-divert --rename --remove /sbin/initctl -
Clean up
apt-get clean rm -rf /tmp/* ~/.bash_history umount /proc umount /sys umount /dev/pts export HISTSIZE=0 exit
-
Unbind mount points
sudo umount $HOME/live-ubuntu-from-scratch/chroot/dev
sudo umount $HOME/live-ubuntu-from-scratch/chroot/run
Create the CD image directory and populate it
-
Access build directory
cd $HOME/live-ubuntu-from-scratch -
Create directories
mkdir -p image/{casper,isolinux,install} -
Copy kernel images
sudo cp chroot/boot/vmlinuz-**-**-generic image/casper/vmlinuz sudo cp chroot/boot/initrd.img-**-**-generic image/casper/initrd -
Copy memtest binary
sudo cp chroot/boot/memtest86+.bin image/install/memtest
Grub configuration
-
Access build directory
cd $HOME/live-ubuntu-from-scratch -
Create image/isolinux/grub.cfg
cat <<EOF > image/isolinux/grub.cfg search --set=root --file /ubuntu insmod all_video set default="0" set timeout=30 menuentry "Try Ubuntu without installing" { linux /casper/vmlinuz boot=casper quiet splash --- initrd /casper/initrd } menuentry "Install Ubuntu" { linux /casper/vmlinuz boot=casper only-ubiquity quiet splash --- initrd /casper/initrd } menuentry "Check disc for defects" { linux /casper/vmlinuz boot=casper integrity-check quiet splash --- initrd /casper/initrd } menuentry "Test memory" { linux /install/memtest } EOF
Create manifest
-
Access build directory
cd $HOME/live-ubuntu-from-scratch -
Generate manifest
sudo chroot chroot dpkg-query -W --showformat='${Package} ${Version}\n' | sudo tee image/casper/filesystem.manifest sudo cp -v image/casper/filesystem.manifest image/casper/filesystem.manifest-desktop sudo sed -i '/ubiquity/d' image/casper/filesystem.manifest-desktop sudo sed -i '/casper/d' image/casper/filesystem.manifest-desktop sudo sed -i '/discover/d' image/casper/filesystem.manifest-desktop sudo sed -i '/laptop-detect/d' image/casper/filesystem.manifest-desktop sudo sed -i '/os-prober/d' image/casper/filesystem.manifest-desktop
Compress the chroot
-
Access build directory
cd $HOME/live-ubuntu-from-scratch -
Create squashfs
sudo mksquashfs chroot image/casper/filesystem.squashfs -
Write the filesystem.size
printf $(sudo du -sx --block-size=1 chroot | cut -f1) > image/casper/filesystem.size
Create diskdefines
-
Access build directory
cd $HOME/live-ubuntu-from-scratch -
Create file image/README.diskdefines
cat <<EOF > image/README.diskdefines #define DISKNAME Ubuntu from scratch #define TYPE binary #define TYPEbinary 1 #define ARCH amd64 #define ARCHamd64 1 #define DISKNUM 1 #define DISKNUM1 1 #define TOTALNUM 0 #define TOTALNUM0 1 EOF
Recognition as an Ubuntu from scratch
-
Access build directory
cd $HOME/live-ubuntu-from-scratch -
Create an empty file named "ubuntu" and a hidden ".disk" folder.
touch image/ubuntu mkdir image/.disk
Create ISO Image for a LiveCD (BIOS + UEFI)
-
Access image directory
cd $HOME/live-ubuntu-from-scratch/image -
Create a grub UEFI image
grub-mkstandalone \ --format=x86_64-efi \ --output=isolinux/bootx64.efi \ --locales="" \ --fonts="" \ "boot/grub/grub.cfg=isolinux/grub.cfg" -
Create a FAT16 UEFI boot disk image containing the EFI bootloader
( cd isolinux && \ dd if=/dev/zero of=efiboot.img bs=1M count=10 && \ sudo mkfs.vfat efiboot.img && \ mmd -i efiboot.img efi efi/boot && \ mcopy -i efiboot.img ./bootx64.efi ::efi/boot/ ) -
Create a grub BIOS image
grub-mkstandalone \ --format=i386-pc \ --output=isolinux/core.img \ --install-modules="linux normal iso9660 biosdisk memdisk search tar ls" \ --modules="linux normal iso9660 biosdisk search" \ --locales="" \ --fonts="" \ "boot/grub/grub.cfg=isolinux/grub.cfg" -
Combine a bootable Grub cdboot.img
cat /usr/lib/grub/i386-pc/cdboot.img isolinux/core.img > isolinux/bios.img -
Generate sha256sum.txt
sudo /bin/bash -c "(find . -type f -print0 | xargs -0 sha256sum | grep -v "\./sha256sum.txt" > sha256sum.txt)" -
Create iso from the image directory using the command-line
sudo xorriso \ -as mkisofs \ -iso-level 3 \ -full-iso9660-filenames \ -volid "Ubuntu from scratch" \ -eltorito-boot \ boot/grub/bios.img \ -no-emul-boot \ -boot-load-size 4 \ -boot-info-table \ --eltorito-catalog boot/grub/boot.cat \ --grub2-boot-info \ --grub2-mbr /usr/lib/grub/i386-pc/boot_hybrid.img \ -eltorito-alt-boot \ -e EFI/efiboot.img \ -no-emul-boot \ -append_partition 2 0xef isolinux/efiboot.img \ -output "../ubuntu-from-scratch.iso" \ -graft-points \ "." \ /boot/grub/bios.img=isolinux/bios.img \ /EFI/efiboot.img=isolinux/efiboot.img