# TubeStats
*A hobby project: Consistency in a YouTube channel*
Shivan Sivakumaran
## Inspiration
- Ali Abdaal
- Consistency - how consistent?
- Getting better as a beginner
- www.tubestats.app
## What does TubeStats do?
1. Takes user input
2. Provides statistics
## 1. User input
```python
# Channel ID
'UCoOae5nYA7VqaXzerajD0lg'
# Link to channel
'https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCoOae5nYA7VqaXzerajD0lg'
# Link to video
'https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=epF2SYpWtos'
# Video ID
'epF2SYpWtos'
```
## 2. Statistics
## How does TubeStats work?
### Part 1 of 2
1. How to set up a development environment?
2. How to access the video information?
3. How to store password and API keys?
4. How do we get and store the video statistics?
## 1. Development environment
```bash
$ mkdir tubestats
$ cd tubestats
$ python3 -m venv venv
$ source venv/bin/activate
$ (venv)
$ git init
```
## 2. Video information
- use `beautifulsoup`, `scraPY`, `selenium`?
- YouTube Data API
- `google-api-python-client`
## 3. Storing API Keys
- Hard code?
- `python-dotenv`
- `.env`
- `.gitignore`
### 3. Storing API keys
```
# .env
API_KEY=xxxxxxxx
```
```python
# tubestats/youtube_api.py
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
API_KEY = os.getenv('API_KEY')
```
## 4. Get YouTube video statistics
- Access API
- Channel upload playlist
- Video statistics
- `pandas` dataframe
### 4. Get YouTube video statistics
```python
import googleapiclient.discovery
load_dotenv()
api_service_name = 'youtube'
api_version = 'v3'
youtube = googleapiclient.discovery.build(
api_service_name,
api_version,
developerKey=os.getenv('API_KEY'))
```
```python [|3|5-16|17-18|20-29|30-32]
# tubestates/youtube_api.py
upload_playlist_ID = channel_data['upload_playlist_ID']
video_response = []
next_page_token = None
while True:
# obtaining video ID + titles
playlist_request = youtube.playlistItems().list(
part='snippet,contentDetails',
maxResults=50, # API Limit is 50
pageToken=next_page_token,
playlistId=upload_playlist_ID,
)
playlist_response = playlist_request.execute()
# isolating video ID
vid_subset = [ vid_ID['contentDetails']['videoId']
for vid_ID in playlist_response['items'] ]
# retrieving video statistics
vid_info_subset_request = youtube.videos().list(
part='snippet,contentDetails,statistics',
id=vid_subset
)
vid_info_subset_response = vid_info_subset_request.execute()
video_response.append(vid_info_subset_response)
# obtaining page token
next_page_token = playlist_response.get('nextPageToken') # get method used because token may not exist
if next_page_token is None:
break
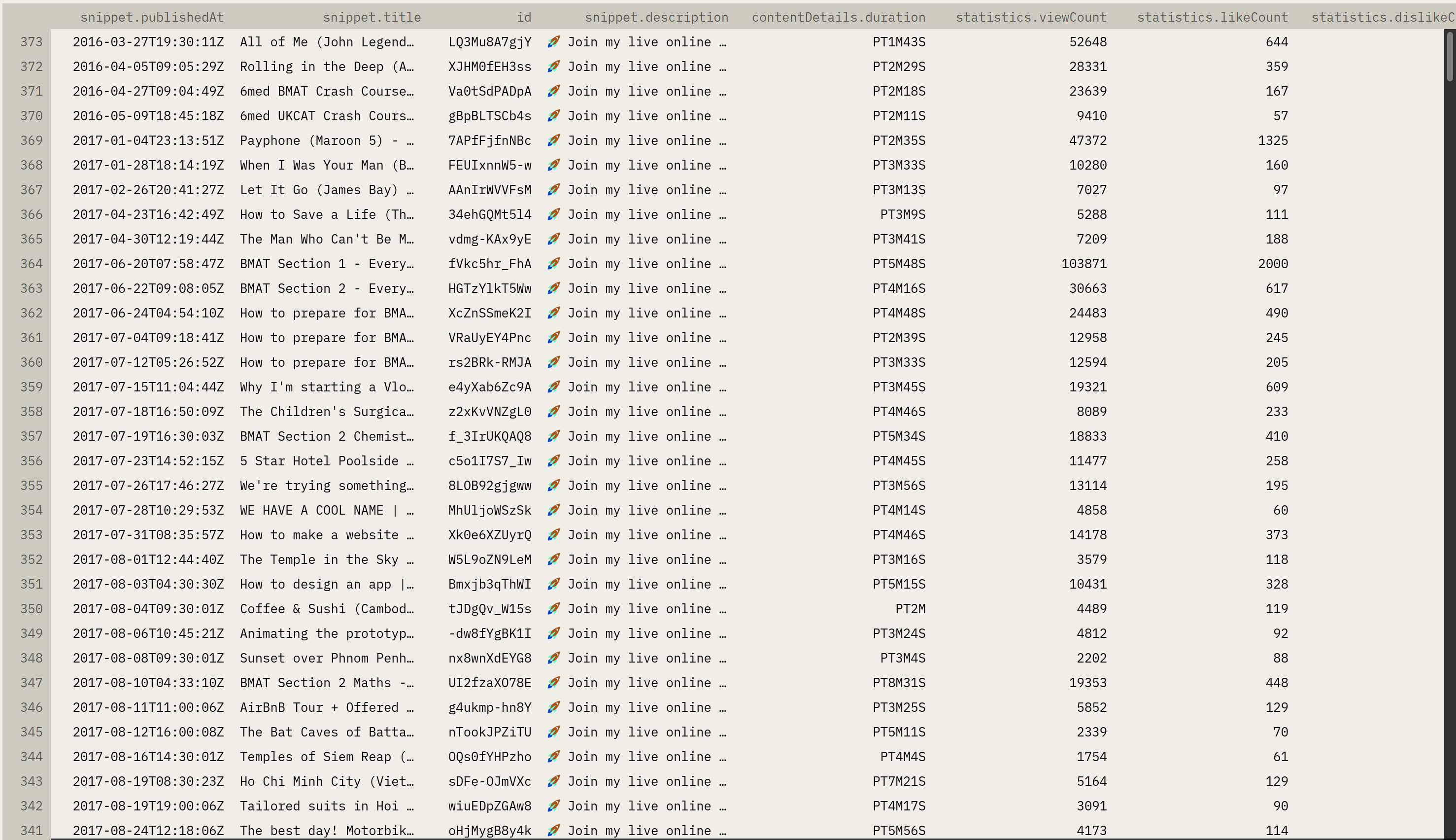
df = pd.json_normalize(video_response, 'items')
return df
### Video statistics
## How does TubeStats work?
### Part 2 of 2
5. How to organise the code?
6. How to test the code?
7. How to display the data and allow interaction?
8. How to account for variable input?
## 5. Organising code
```bash [1-9|10-15|16-20|21]
tubestats/
├── data
│ ├── channel_data.pkl
│ └── video_data.pkl
├── LICENSE
├── Procfile
├── README.MD
├── requirements.txt
├── setup.sh
├── tests
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── test_settings.py
│ ├── test_youtube_api.py
│ ├── test_youtube_data.py
│ └── test_youtube_parser.py
├── tubestats
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── youtube_api.py
│ ├── youtube_data.py
│ └── youtube_parser.py
└── youtube_presenter.py
## 6. Testing
```python [|15-20]
# tests/tests_youtube_api.py
from tubestats.youtube_api import create_api, YouTubeAPI
from tests.test_settings import set_channel_ID_test_case
from pathlib import Path
import pytest
import googleapiclient
import pandas
def test_create_api():
youtube = create_api()
assert isinstance(youtube, googleapiclient.discovery.Resource)
@pytest.fixture()
def youtubeapi():
channel_ID = set_channel_ID_test_case()
yt = YouTubeAPI(channel_ID)
return yt
def test_get_video_data(youtubeapi):
df = youtubeapi.get_video_data()
assert isinstance(df, pandas.core.frame.DataFrame)
# saving video data to save API calls for later testing
BASE_DIR = Path(__file__).parent.parent
df.to_pickle(BASE_DIR / 'data' / 'video_data.pkl')
## 7. Sharing to the world
- graphs with tool tips, `altair`
- creating interaction with `streamlit`
- hosting on Heroku
### 7. Sharing to the world
```python []
# tubestats/youtube_data.py
import altair as alt
def scatter_all_videos(self, df: pd.core.frame.DataFrame) -> alt.vegalite.v4.Chart:
df_views = df
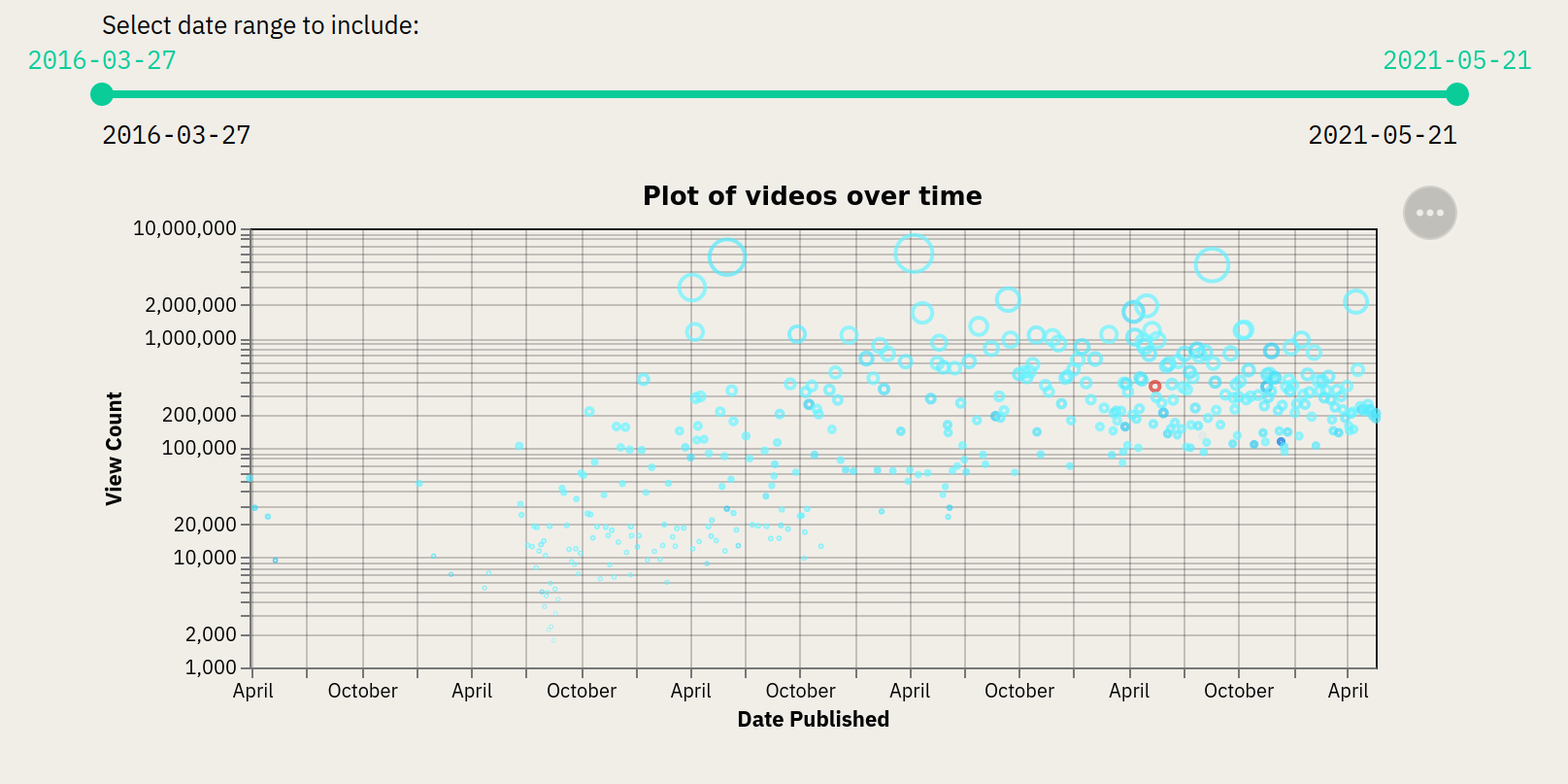
c = alt.Chart(df_views, title='Plot of videos over time').mark_point().encode(
x=alt.X('snippet\.publishedAt_REFORMATED:T', axis=alt.Axis(title='Date Published'), scale=alt.Scale(type='log')),
y=alt.Y('statistics\.viewCount:Q', axis=alt.Axis(title='View Count')),
color=alt.Color('statistics\.like-dislike-ratio:Q', scale=alt.Scale(scheme='turbo'), legend=None),
tooltip=['snippet\.title:N', 'statistics\.viewCount:Q', 'statistics\.like-dislike-ratio:Q'],
size=alt.Size('statistics\.viewCount:Q', legend=None)
)
return c
### 7. Sharing to the world
```python [|5-14|16-19]
# youtube_presenter.py
import streamlit as st
def date_slider(date_end=datetime.today()):
date_start, date_end = st.slider(
'Select date range to include:',
min_value=first_video_date, # first video
max_value=last_video_date, #value for date_end
value=(first_video_date , last_video_date), #same as min value
step=timedelta(days=2),
format='YYYY-MM-DD',
key=999)
return date_start, date_end
date_start, date_end = date_slider()
transformed_df = youtuber_data.transform_dataframe(date_start=date_start, date_end=date_end)
c = youtuber_data.scatter_all_videos(transformed_df)
st.altair_chart(c, use_container_width=True)
### 7. Sharing with the world
```shell []
$ streamlit run youtube_presenter.py
You can now view your Streamlit app in your browser.
Local URL: http://localhost:8501
Network URL: http://192.0.0.0.1
### 7. Sharing to the world
```bash
$ (venv) pip freeze > requirements.txt
```
```bash
# setup.sh
mkdir -p ~/.streamlit/echo "\
[server]\n\
headless = true\n\
port = $PORT\n\
enableCORS = false\n\
\n\
" > ~/.streamlit/config.toml
```
```bash
# Procfile
web: sh setup.sh && streamlit run youtube_presenter.py
```
```bash
$ heroku login
$ heroku create tubestats
$ git push heroku main
```
## 8. Different user input
- taking video ID
- URL links
- using regex, `re` module
### 8. Different user input
```python []
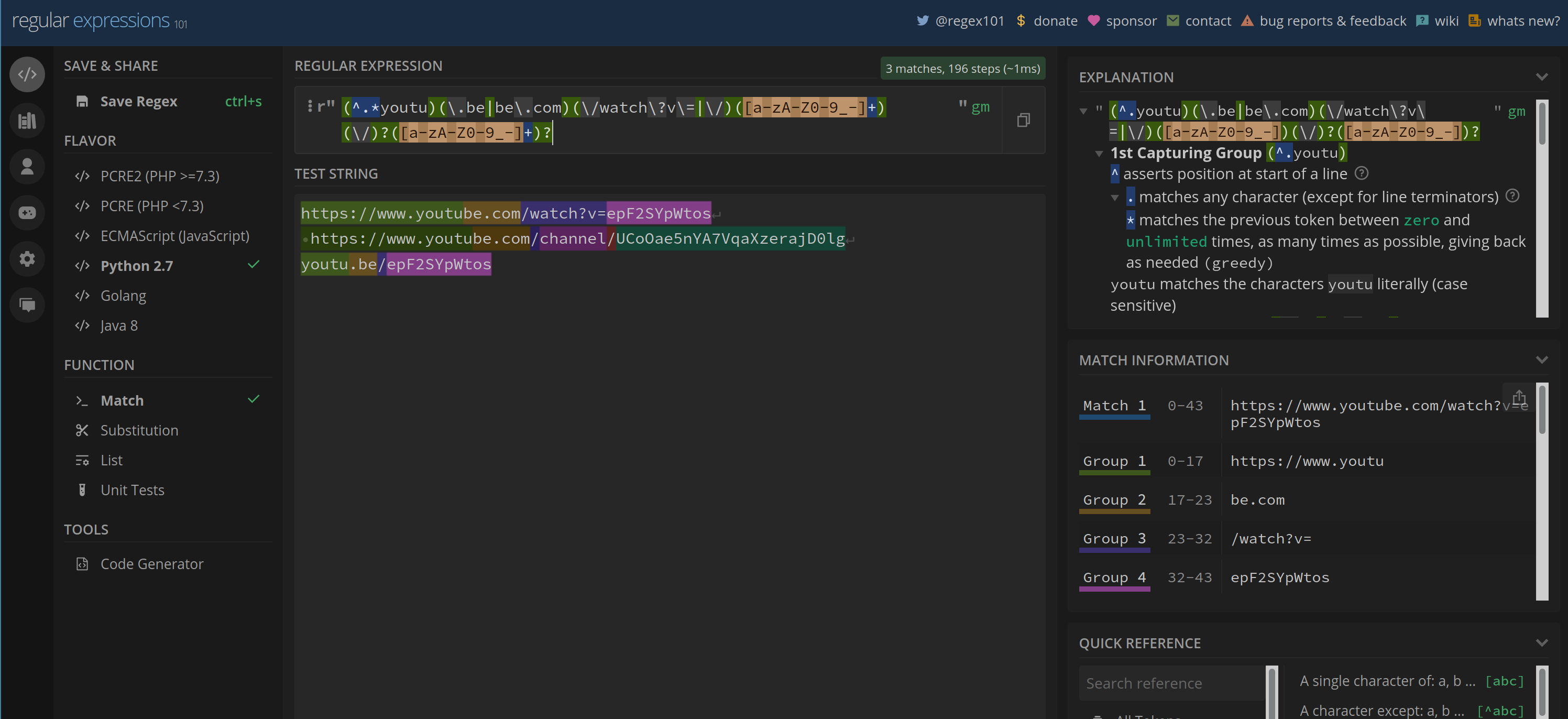
import re
LINK_MATCH = r'(^.*youtu)(\.be|be\.com)(\/watch\?v\=|\/)([a-zA-Z0-9_-]+)(\/)?([a-zA-Z0-9_-]+)?'
m = re.search(LINK_MATCH, for_parse)
video_id = m.group(4) # video ID
if video_id == 'channel':
return m.group(6) # Channel ID
elif video_id == 'user':
channel_username = m.group(6) # Channel Username
### 8. Different user input
## Things to consider for the future
- Error handling
- Maxing API calls
- Comparing different channels
- DataFrame and memory
### DataFrame immutability and memory?
```python []
df = self.df
df = df[['snippet.publishedAt',
'snippet.title',
...
'statistics.favoriteCount',
'statistics.commentCount']]
df = df.fillna(0)
df = df.astype({'statistics.viewCount': 'int',
...
'statistics.commentCount': 'int',})
df['statistics.viewCount_NLOG'] = df['statistics.viewCount'].apply(lambda x : np.log(x))
df = df.sort_values(by='snippet.publishedAt_REFORMATED', ascending=True)
## What did I learn
- Project based learning
- 'minimal viable product'
## Conclusion
- Analysing consistency
- YouTube Data API --> pandas --> altair --> Heroku
- Share your work!
## Acknowledgements
- Menno Finlay-Smits